Web Based Computer Aided Instruction for Web Application Development
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
Recent advances in information technology (IT) provide educators with unique opportunities to fundamentally shape education of the future. If used intelligently, the new computer technology will usher in revolutionary changes in education—the way we teach and learn—at all levels: kindergarten to high school, and university to life-long learning. The emergent components of computer-aided education (CAE) including multimedia presentations, interactive digital books, and the internet, are often developed separately to be used as individual approaches in CAE without a cohesive and comprehensive strategy. The key to effective CAE in the future lies in an integration of these three technologies to form a unified approach to education.
An integrated approach will give students of ecology and science a comprehensive learning environment that includes in-class, independent, and extended learning. I have developed extensive computer-aided, multimedia, instructional modules to teach my courses in introductory general ecology physiological plant ecology, and restoration ecology. The use of computer-aided education, including interactive multimedia lessons and modules for independent learning, provides students with an enhanced in-class lectures and the opportunity to extend learning beyond the classroom. Each course has a companion course on internet from which students can access course materials and information at their convenience. Further enhancements to the courses on internet will soon extend the student’s opportunities for learning beyond the classroom.
As with any field of learning, acronyms abound in the computer assisted instruction/learning domain. Terms vary in the breadth of their definition, the term Computer Aided Instruction will be used in this document as an inclusive term unless specifically stated.
Many of the concepts that prevail in CALL also pertain to CAI. The researchers believe that it is helpful to look at the common concepts before focusing on the CALL specific ones.
Computer Aided Instruction, as the name suggests, is the use of a computer to provide instruction. The format can be from a simple program to teach typing to a complex system that uses the latest technology to teach new keyhole surgery techniques. CAI draws on knowledge from the fields of learning, cognition, Human Computer Interaction (HCI) amongst others. Many of the major themes in CALL are reflected in the field of CAI.
Computer Aided Instruction (CIA), diverse and rapidly expanding spectrum of computer technologies that assist the teaching process. CAI is also known as computer-assisted instruction. Example of CAI applications includes guided drill and practice exercise, computer visualization of complex objects, and computer-facilitated communication between students and teachers.
Computer Aided instruction that helps teach or encourage interaction can be presented on computers in the form of text or in multimedia formats, which include photographs, videos, animation, speeches, and music. The guided drill was a computer program that poses questions to students, returns feedback, and selects additional questions based on the students’ responses. Recent guided drill systems incorporate the principles of education in addition to subject matter knowledge into the computer program.
Computer also helps students visualize objects that are difficult or impossible to view. For example, computers can be used to display human anatomy, molecular structures, or complex geometrical objects. Exploration and manipulation of simulated environments can be accomplished with CAI-ranging from virtual laboratory experiments that may be too difficult, expensive, or dangerous to perform in a school environment to complex virtual worlds like those used in airplane flight simulation.
Computer Aided Instruction tools, such as word processors, spread sheets, and databases, collect, organized, analysed, and transmit information. They also facilitate communication among students, between students and instructors, and beyond the classroom.
PROJECT CONTEXT
Computer Aided Instruction brings with it several potential benefits as a teaching/learning medium. These include self-paced learning, self-directed learning, the exercising of various senses and the ability to represent content in a variety of media. Although Computer Aided Instruction has not been studied in the EL community situation, many of the benefits in the general Computer Aided Instruction context should also be available in the EL one.
With self-paced learning, learners can move as slowly or as quickly as they like through a program. If they want to repeat some task or review some material again, they can do so as many times as they choose. The program will not tire or complain about repetitions. Learners can skip over a topic if information is already known, making the learning process more efficient. With self-directed learning, learners can decide what they want to learn and in what order.
Learners have different learning styles and use different learning strategies. Various studies (Entwistle, 1981; Schmeck 1988; Ford and Chen, 2001) have shown that when learners can learn in a way that suits them, improvements in the effectiveness of the learning process normally ensue.
Humans are multi-sensory animals. The more senses through which we receive information, the easier it is to remember. According to Fletcher (1990), people remember 20% of what they hear, 40% of what they see and hear and 75% of what they see, hear and do. The fact that the computer can exercise various senses and present information in a variety of media can enhance the learning process. Meskill and Mossop (1997) report that computers encourage learning as they provide a stimulating environment and promote enthusiasm. Computers may help the reticent student who is afraid to make mistakes in a classroom situation (Chun, 1994; Meskill and Swan, 1996). They are good for online reference which useful in a language learning situation (for example, online dictionaries (Leffa, 1992)).
PURPOSE AND DESCRIPTION
This study Computer Aided Instruction aims the following:
1) Analyze design and development computer assisted instruction on introduction to wed-based application subject.
2) To evaluate the efficiency of package.
3) To evaluate learning effectiveness from education computer instructional package and
4) To determine learners satisfaction towards the package.
The research tools used in this study are the following:
1) The computer assisted instruction on web-based application subject
2) The achievement tests, and
3) The questionnaire for the learner’s satisfaction.
Computer Aided Instruction refers to the use of the computer as a tool to facilitate and improve instruction it uses a combination of text, graphics, sound and video in enhancing the learning process. The computer has many purposes in the classroom, and it can be utilized to help a student in all areas of the curriculum.
Computer Aided Instruction refers to the use of the computer as a tool to facilitate and improve instruction. Computer Aided Instruction programs use tutorials, drill and practice, simulation, and problem solving approaches to present topics, and they test the student’s understanding. Use of computer in education is referred by many names such as Computer Assisted Instruction (CAI), Computer Aided Instruction (CAI), Computer Assisted Learning (CAL), Computer Based Education (CBE), Computer Based
Instruction (CBI), Computer Enriched Instruction (CEI), Computer Managed Instruction (CMI) New Terminology such as; Web Based Training, Web Based Learning, and Web Based Instruction.
Computer Aided Instruction programs use tutorials, drill and practice, simulation, and problem solving approaches to present topics, and they test the student’s understanding such as one-to-one interaction, great motivator, freedom to experiment with different options, instantaneous response/immediate feedback to the answers elicited, Self pacing that allow students to proceed at their own pace, Helps teacher can devote more time to individual students, Privacy helps the shy and slow learner to learns, Individual attention, learn more and more rapidly and multimedia helps to understand difficult concepts through multi-sensory approach.
A typical CAI provides text or multimedia content, multiple-choice questions, problems, immediate feedback, notes on incorrect responses, summarizes students’ performance, exercises for practice, Worksheets and tests, and self-directed learning – students can decide when, where, and what to learn.
OBJECTIVES
This study aims to design and develop a computer assisted instruction on introduction on web-based application subject with the following objectives.
- To evaluate the efficiency of Computer Aided Instruction on web-based application subject according to:
- Simulation
- Tutorial/Trivia
- Drill and Practice
- Problem Solving
- Discovery
- To evaluate learning effectiveness of computer aided instructions according to:
- System functionality
- System Usability
- Ease of use
- User interfaces
- System Security
- To determine learners satisfaction towards the computer aided instruction on web-based application subject when group according to:
- Gender
- Age
SCOPE AND LIMITATIONS
This study focuses on Computer Aided Instruction (CAI) on the introduction to web-based application subject as an instructional technique whereby a computer is used to present the instructional material and monitor the learning that takes place.
This limits on the introduction to web-based application subject for information technology third year students and teacher of the academic institution.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND SYSTEMS
Utilization of CAI developed for specific course objectives coincided closely with course content, which is an indication of the effectiveness of the applications in achieving their curricular objectives. In contrast, student use of tutorials coincided most closely with in-course examinations. Students’ responses to surveys were generally substantiated by server statistics, but discrepancies were sufficiently large (10% to 20%) to call into question the validity of these surveys. Significant differences in CAI utilization correlated with the performances of students in the course. This study demonstrates an important advantage of web-based applications to collect and evaluate CAI utilization efficiently and objectively at both the level of the class and the level of the individual student.
Computers are a familiar sight in classrooms in the twenty-first century, and technology has been used to streamline many educational tasks. There are different types of educational computer use, and not every use of a computer in the classroom is considered computer-assisted instruction. The educational uses of computers that are considered to be computer-assisted instruction (CAI) or computer-based instruction (CBI) are those cases in which either instruction is presented through a computer program to a passive student, or the computer is the platform for an interactive and personalized learning environment.
Within the broad definition, computer aided instruction may follow different paths to the same end. One example is how computer aided instruction is used in relation to other teaching presentations. CAI can be used either in isolation, bearing the whole responsibility for conveying instruction to students, or in combination with conventional, i.e., face-to-face, teaching methods. Research has shown that the combination of conventional and CAI instruction has been most effective in raising student achievement scores.
Computer-assisted instruction is used through the entire range of education from preschool to professional school. It has been offered in a wide variety of fields, including all the main school subjects taught in elementary and secondary schools. At CALI, the Center for Computer-Assisted Legal Instruction, law students from across the United States and other countries such as Belgium, Brazil, Canada, China, Denmark, Ireland, Kenya, Korea, Mexico, the Netherlands, Nigeria, Russia, Singapore, South Africa, Sweden, and Taiwan have access to CAI law school lessons to supplement their instruction.
Computer-assisted instruction has also been growing in use in a wide number of employment areas. It has been used to teach novice nurses how to perform intravenous injections, to teach jet engine mechanics in the US Air Force maintenance tasks, and to provide safety instruction for food service workers in an urban hospital.
CAI can also focus on smaller segments of the population. Computer-assisted instruction has also been used to personalize learning for people with learning disabilities, language limitations, and physical limitations. In the latter case, screen-reading programs may cater to sight-impaired users, and a variety of specialized
Interactive devices, such as roller balls, joysticks, and oversized keyboards may be used by a person when a mouse or standard keyboard presents a challenge.
Different types of computer-assisted instruction typically involve various subjects and the ways in which computers can be used to best assist in learning those subjects. This includes English, mathematics, science, and history that can all be enhanced beyond traditional classroom lessons by learning through the use of computer systems. Within these subject areas, however, there are also different approaches that can be utilized for computer-assisted instruction, such as sample problems for math and science, interactive maps and timelines for history, and numerous writing activities for English and other languages. These instruction methods can also demonstrate a wide range of interactive features as well.
Computer-assisted instruction refers to a form of learning that utilizes computers, and is typically intended as a way to supplement traditional teacher-based learning. This is in contrast to computer-based systems often developed to make the computer learning the primary method for students. Many forms of computer-assisted instruction are provided with textbooks and other learning systems, often as a media disc that can be used with a computer or downloadable programs and files from a related website.
Common types of computer-assisted instruction are based on the subject matter presented in these programs. Mathematics, for example, often utilizes interactive programs that present math problems for students and provides them with tools to answer the problem. These programs grant real-time feedback based on the information the
Student enters, allowing for faster responses than what is generally allowed by traditional classrooms and teachers. Science lessons can also be facilitated through such programs, and physical sciences such as chemistry and physics often utilize systems similar to those found in math. Other types of computer-assisted instruction can be found in language studies and history. Studies of English and other languages can often use computer programs that provide sample sentences that are missing words, into which the student can input words and receive feedback based on the accuracy of the word. More interactive games and lessons can also be provided that stress vocabulary development and understanding of different sentence structures. History lessons that utilize computer-assisted instruction can include an interactive timeline that lets students select an event or period and then provides audio and video about that time. There are even interactive games that allow students to explore different times through the game interface.
Computer-assisted instruction can also be used to assist students who may have special needs for learning. Various disabilities can be partially overcome through different forms of technology, and concentrated, reinforced learning can often be more easily facilitated through a computer program than from an instructor. When this type of instruction is paired with the lessons and efforts of a trained teacher, then the benefits become even more pronounced.
Computer-assisted teaching refers to instruction that is delivered partially or totally through the medium of a computer. This method of teaching occurs in all levels of education from primary to post-secondary courses. While many students benefit from
Course material presented through the computer or over the Internet, there are some difficulties in implementing computer assisted instruction (CAI) in certain educational settings. Some teachers who have implemented computer-assisted teaching to help deliver course content have struggled with learning the technology to effectively utilize those programs. In addition, some teachers have noted increased levels of student anxiety when encountering the computer programs. Even well-designed programs will occasionally have a problem which can interfere with curriculum schedules and assignment deadlines. Although computer-assisted teaching can offer students who have limited computer skills an opportunity to increase their comfort level with computers, teachers ought to be prepared for a steep classroom learning curve if their students are not adept at using the equipment and navigating online.
Other teachers struggle to find software that fits the needs of the course. Not all programs are well aligned with curricular goals, and the front-end cost of buying software for a school can be quite steep. Fortunately, many software companies will allow instructors and students to test their products before making a purchase. This allows the school to make an informed decision about the software they’d like to purchase.
Students can become bored sitting in a classroom for hours. Teaching aids can provide a welcome break for students who have been sitting for a while and listening to an instructor lecture in front of the room. Educators can use various teaching aids besides textbooks to pique students’ interest and demonstrate how things work. Visual aids, such as whiteboards or chalkboards, charts, maps, flash cards, and calendars are commonly used. Presentation tools such as bulletin boards, audio-visual equipment, and overhead projectors are also utilized frequently along with multimedia displays and computers.
Flash cards are an effective way to teach various subjects. These popular teaching aids are available for many fields, such as spelling, geography, and arithmetic, and the teacher or parent can also create customized flash cards geared toward a specific subject or child. Children who are visual learners will receive the most benefit from the use of flash cards, but auditory learners will also benefit if the information presented on the cards is read aloud.
A pointer is a teaching aid used in many classrooms. It is used to point out items such as words written on a chalkboard or features on a map. The traditional pointer is a long, skinny wand. Laser pointers, which are used to shine a beam of light on the feature the instructor wants to highlight, are becoming more common. The lights in laser pointers are available in different colours, and some can even display various designs such as flowers, butterflies, and animals.
Computers have become popular teaching aids, but overhead projectors still have a place in the classroom. A transparency is placed on the glass and the information on the transparency is projected onto a screen. An instructor can write the information directly onto the transparency. The transparency can also be fed into a laser printer so that information can be transferred onto the transparency from a computer.
Some teaching aids are aimed at a specific subject. For example, driving simulators have been developed for use in driver’s education classes. The student sits in a module that has a steering wheel, accelerator pedal, and brake pedal and watches a movie from the perspective of a driver.
He or she reacts to events taking place on the screen by pressing the accelerator or brake and turning the steering wheel. The driving simulator records all of the students’ actions for the teacher to review with the student afterward.
Computer-assisted language learning is a rapidly growing field. As new software and technologies continue to improve, online courses have become increasingly popular.
Common modes of online language learning include online remote instruction, study software, and online tools for language students.
Many universities, private companies, and cultural organizations offer online computer-assisted language learning by means of distance education classes. These classes can generally be taken independently or as part of an online degree. Costs and quality of online degree programs vary wildly. Some programs are accredited, but others are not. Accreditation can be a good indicator of the quality of a course and will help ensure that the course can be used towards a university degree.
The two main varieties of online distance education classes are synchronous and asynchronous. Both are computer-assisted language learning, but the use of the computer varies somewhat. Asynchronous courses frequently use a computer to deliver texts or pre-recorded lectures. These courses also frequently employ some degree of computer graded assessment.
Synchronous online language learning courses require students to participate in real time or near real time classroom activities. Computer-assisted language learning technologies employed in these courses include student forums, live multicast lectures with student interaction, and one-on-one or group video chat. The additional human involvement required to run these courses can make them more expensive, but they can provide more extensive student feedback than asynchronous courses.
Another major area of computer-assisted language learning is note taking and study software. Note taking software allows students to record portions of live or online lectures and write associated notes to be stored with the recording. This can be especially helpful when studying pronunciation.
Study software includes flash card software, character recognition software, and computer-based dictionaries and translators. Flash card software is helpful for students learning new vocabulary. Many flash card programs use a spaced repetition algorithm to improve memorization by detecting which words are hardest for each student and showing those words most often. Various flash card programs are available at a variety of price points, ranging from a moderate monthly fee to a free download.
Students learning languages which use different writing systems may benefit from character recognition software. When combined with flash card software, this allows students to use a spaced repetition algorithm while learning new characters. It can also help students move from recognizing characters to easily writing them.
Advanced students studying texts often use computer based dictionaries to look up unknown words. These dictionaries can be much faster to use than traditional paper dictionaries. Online translation tools are generally not reliable for detailed translations but can help students who are not very familiar with a language confirm that they have not used incorrect words in their compositions.
Different types of computer-assisted instruction typically involve various subjects and the ways in which computers can be used to best assist in learning those subjects. This includes English, mathematics, science, and history that can all be enhanced beyond traditional classroom lessons by learning through the use of computer systems. Within these subject areas, however, there are also different approaches that can be utilized for computer-assisted instruction, such as sample problems for math and science, interactive maps and timelines for history, and numerous writing activities for English and other languages. These instruction methods can also demonstrate a wide range of interactive features as well.
Computer-assisted instruction refers to a form of learning that utilizes computers, and is typically intended as a way to supplement traditional teacher-based learning. This is in contrast to computer-based systems often developed to make the computer learning the primary method for students. Many forms of computer-assisted instruction are provided with textbooks and other learning systems, often as a media disc that can be used with a computer or downloadable programs and files from a related website.
Common types of computer-assisted instruction are based on the subject matter presented in these programs. Mathematics, for example, often utilizes interactive programs that present math problems for students and provides them with tools to answer the problem. These programs grant real-time feedback based on the information the student enters, allowing for faster responses than what is generally allowed by traditional classrooms and teachers. Science lessons can also be facilitated through such programs, and physical sciences such as chemistry and physics often utilize systems similar to those found in math.
Other types of computer-assisted instruction can be found in language studies and history. Studies of English and other languages can often use computer programs that provide sample sentences that are missing words, into which the student can input words and receive feedback based on the accuracy of the word. More interactive games and lessons can also be provided that stress vocabulary development and understanding of different sentence structures. History lessons that utilize computer-assisted instruction can include an interactive timeline that lets students select an event or period and then provides audio and video about that time.
There are even interactive games that allow students to explore different times through the game interface.
Computer-assisted instruction can also be used to assist students who may have special needs for learning. Various disabilities can be partially overcome through different forms of technology, and concentrated, reinforced learning can often be more easily facilitated through a computer program than from an instructor. When this type of instruction is paired with the lessons and efforts of a trained teacher, then the benefits become even more pronounced.
Information that helps teach or encourages interaction can be presented on computers in the form of text or in multimedia formats, which include photographs, videos, animation, speech, and music. The guided drill is a computer program that poses questions to students, returns feedback, and selects additional questions based on the students’ responses. Recent guided drill systems incorporate the principles of education in addition to subject matter knowledge into the computer program.
Computers also can help students visualize objects that are difficult or impossible to view. For example, computers can be used to display human anatomy, molecular structures, or complex geometrical objects. Exploration and manipulation of simulated environments can be accomplished with CAI-ranging from virtual laboratory experiments that may be too difficult, expensive, or dangerous to perform in a school environment to complex virtual worlds like those used in airplane flight simulators.
CAI tools, such as word processors, spread sheets, and databases, collect, organize, analyse, and transmit information. They also facilitate communication among students, between students and instructors, and beyond the classroom
Humans are multi-sensory animals. The more senses through which we receive information, the easier it is to remember. According to Fletcher (1990), people remember 20% of what they hear, 40% of what they see and hear and 75% of what they see, hear and do.
The fact that the computer can exercise various senses and present information in a variety of media can enhance the learning process. Meskill and Mossop (1997), reported that computers encourage learning as they provide a stimulating environment and promote enthusiasm. Computers may help the reticent student who is afraid to make mistakes in a classroom situation (Chun, 1994; Meskill and Swan, 1996). They are good for online reference which useful in a language learning situation (for example, online dictionaries (Leffa, 1992)).
According to Beth Wilson (1998), she stated that thoughtfully designed computer software can presented multiple, dynamically linked representation in ways that are impossible with static, inert media such as books and chalkboards. Some of the most fruitful applications of computer technology derive its capacity to present educational powerful, dynamic visual images particularly in science and math.
Computer Aided Instruction has a potential to serve a dual purpose by enhancing the learning experience for resident students, while opening the educational experience up to distance students. Brahler(2005).
Many Classification of computer aided instruction (CAI) available in the market. According to Spiro and Jehng (1990), it seems to be most often utilized for educational purposes such as:
Drill and practices, instructional programs simply assisted the student in remembering and utilizing information that the teacher has already presented, reinforcing previous learning through repetition. It is the most important to improving knowledge level.
Tutorial, were designed to introduce unfamiliar subject matter. The format of a computer tutorial often emulates a dialogue between the computer and the student. Information is presented, questions were asked to the student and the basis of the responses given. A decision is made to move on to the new material or review what has already been presented.
Games, presented course content in a competitive and entertaining manner, in an effort to maintain a high level of student interest. Though most frequently used to reinforce factual knowledge at the lower levels of the taxonomy, it was quite possible to create instructional games that demand application skills from all levels.
These first computer aided instruction types were the most successful at improving the knowledge and comprehension levels of blooms taxonomy. Games presented course content in a competitive and entertaining manner, in an effort to maintain a high level of student interest. Though most frequently used to reinforce factual knowledge at the lower levels of the taxonomy, it was quite possible to create instructional games that demand application skills from all levels.
Simulation, requires the student to apply acquired knowledge to a novel situation. As a result the student must analyse a presented scenario, make decisions based on the information given and determine a course of action. The simulated environment must change based on the course of action taken, presenting a significant challenge to the programmer.
Problem-solving, requires the student to used high level of cognitive abilities in the process of considering the problem at hand, analyzing the problem situation and its various solutions, predicting respective outcomes, determining which specific plan to attempt, and enacting the appropriate actions, Shute (1993). Well-designed software that fits this classification may require abilities from all level of the taxonomy. However according to Jones (1990), the best way to have s student used abilities of synthesis was to have his/her created novel hypertext system. In this case student was forced to identify relationships and evaluate all aspects of the chosen set of course materials. Evaluate ability that can be tested and improved through programs representing any of these five types of computer aided instruction by promoting students at significant time during the session and providing appropriate feedback or explanation.
Discovery-environment, in addition to the delineated types of CAI, it was also possible to provide a discovery environment, (Kindall, 1987), within which the student
was given a high level of freedom in determining the specific information presented during session, as well as order of presentation, (Spiro & Jehng, 1990).
According to Thomas (1979), he reported that computer aided instruction was associated with achievement levels equal to or higher that traditional instruction. In addition, he reported also that the attitude towards computer and the subject matter, a reduction in time to master content and comparable levels of retentions was improved.
CHAPTER III
TECHNICAL BACKGROUND
Computer Aided Instruction CAI, as the name suggests, was the use of a computer to provide instruction. The format can be from a simple program to teach typing to a complex system that uses the latest technology to teach new keyhole surgery techniques. CAI was drawn knowledge from the fields of learning, cognition, Human Computer Interaction (HCI) among others. Many of the major themes in CALL were reflected in the field of CAI.
Themes common to both were explored in this chapter and themes specific to CALL are explained in With self-paced learning, learners can move as slowly or as quickly as they liked through a program. If they want to repeat some task or review some material again, they can do so as many times as they choose. The program will not tired or complain about repetitions. Learners can skip over a topic if information was already known, making the learning process more efficient.
With self-directed learning, learners decided what they want to learn and in what order. As will be shown later in this chapter, learners have different learning styles and used different learning strategies.
Various studies (Entwistle, 1981; Schmeck 1988; Ford and Chen, 2001) have shown that when learners can learn in a way that suits them, improvements in the effectiveness of the learning process normally.
CHAPTER IV
METHODOLOGY
The chapter discuss the method used in this study, the population and the locale of the study, sampling procedure, analysis of data, the requirement analysis, the design software with processes, development and testing, the description of prototype, the implementation plan and the , implementation result.
POPULATION AND THE LOCALE OF THE STUDY
The unit of analysis in this study was the third year Bachelor of Science in Information Technology students. In the sense that, we are now in the global competitiveness and computer technology was one of the tools of being competent.
SAMPLING PROCEDURE
Sampling is the process of choosing a portion of a target population (Garcia and Reganit, 2010), Sampling is also the process of choosing a representative portion of a population or some elements in a population they will represent the entire population (David, 2006). It is assumed that the characteristics of the chosen elements called sample, reflects the characteristics of the entire population.
To determine the sample size, the researcher will utilized, the formula of Sloven from each groups, with the margin of error is 5% or 0.05.
Design of Software and Processes
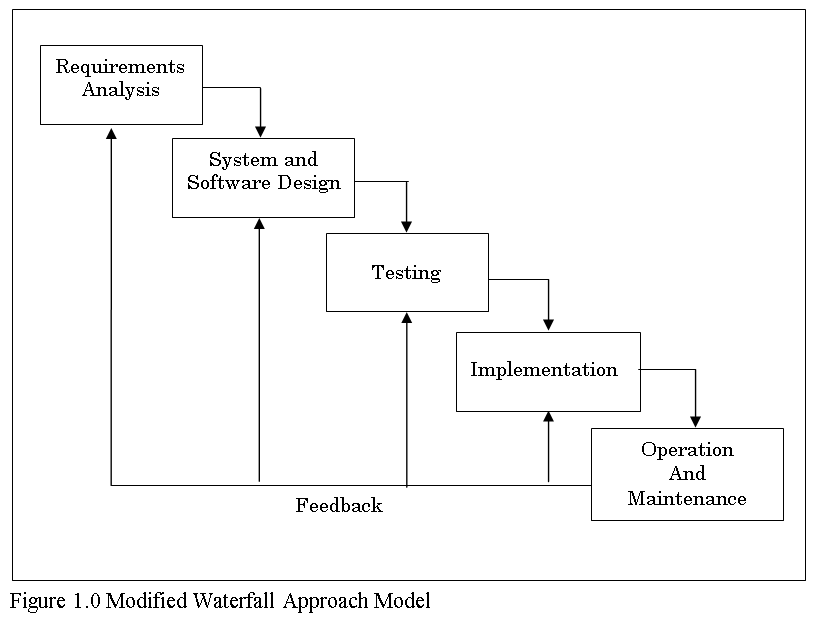
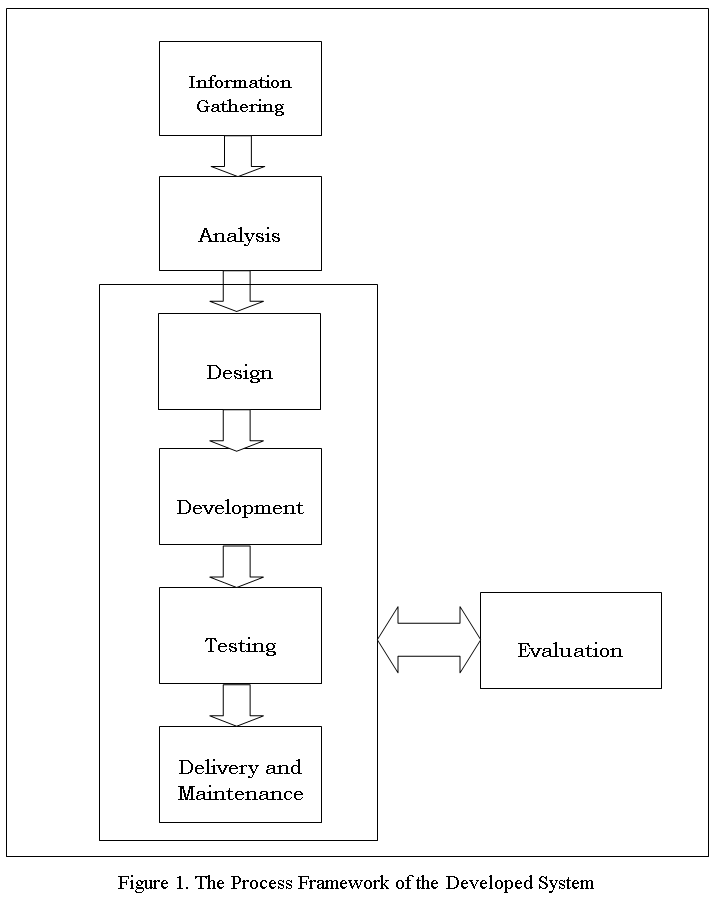
This chapter introduces the systems methodology. The researcher used is a software process model was an abstract representation of a process. It presents a description of a process from some particular perspective such as: Specification, Design, Validation and Evolution. There are many variants of these models. A formal development where a waterfall-like process was used, but the specification was formal that was refined through several stages to an implementable design, this model are chosen because their features corresponds to most software development programs.
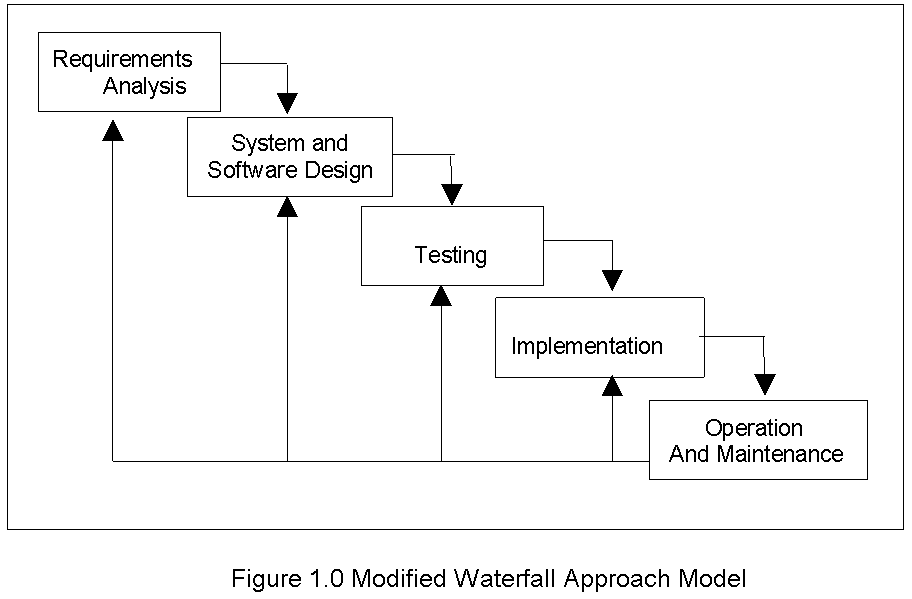
The waterfall model was the classical model of software engineering. This model was one of the oldest models and it was widely used in government projects and in many major companies. As this model emphasizes planning in early stages, it ensures design flaws before they develop. In addition, its intensive document and planning make it work well for projects in which quality control is a major concern.
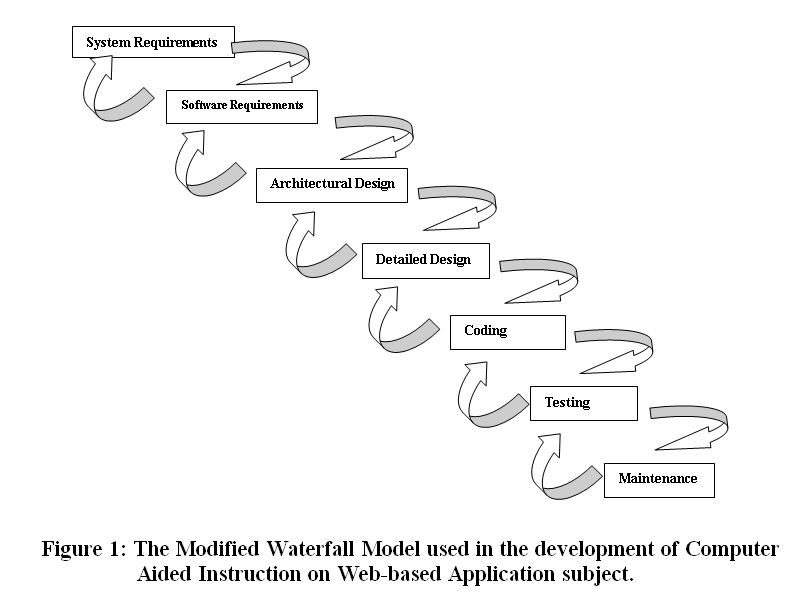
The pure waterfall lifecycle consists of several non-overlapping stages. The model begins with establishing system requirements and software requirements and continues with architectural design, detailed design, coding, testing, and maintenance. The waterfall model serves as a baseline for many other lifecycle models.
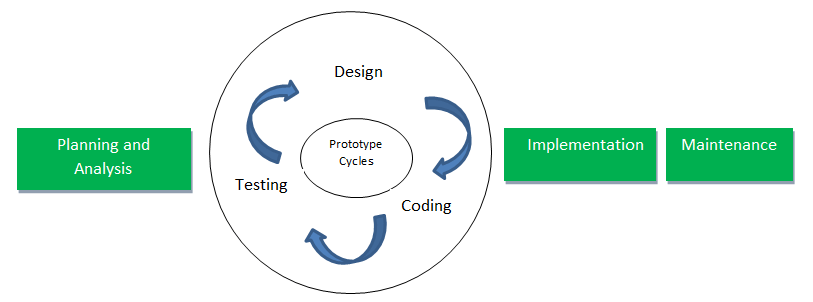
![The Modified Waterfall Model used in the development of Computer Aided Instruction on Web-based Application subject]()
The Modified Waterfall Model used in the development of Computer Aided Instruction on Web-based Application subject
Figure 1: The Modified Waterfall Model used in the development of Computer Aided Instruction on Web-based Application subject.
System requirements. Established the component for building the system, it included the hardware requirements, software tools, and other necessary components. Examples include decisions on hardware, such as plug-in boards (number of channels, acquisition speed, and so on), and decisions on external pieces of software, such as databases or libraries.
Software requirements: Establishes the expectations for software functionality and identifies which system requirements the software affects.
Requirements analysis included the determining interaction needed with other applications and databases, performance requirements, user interface requirements, and so on.
Architectural design. Determine the software framework of a system to meet the specific requirements. This design defines the major components and the interaction of those components, but it does not define the structure of each component. The external interfaces and tools used in the project can be determined by the designer.
Detailed design. Examines the software components defined in the architectural design stage and produced a specification for how each component was implemented.
Coding. Implement the detailed design specifications.
Testing. Determines whether the software meets the specified requirements and finds any errors presented in the code.
Maintenance. Addressed problems and enhancement requests after the software released. In some organizations, a change control board maintains the quality of the product by reviewing each change made in the maintenance stage. Consider applying the full waterfall development cycle model when correcting problems or implementing these enhancement requests. In each stage, documents that explain the objectives and describe the requirements for that phase were created. At the end of each the stage, reviews was implemented to determine whether the project would proceed to the next stage.
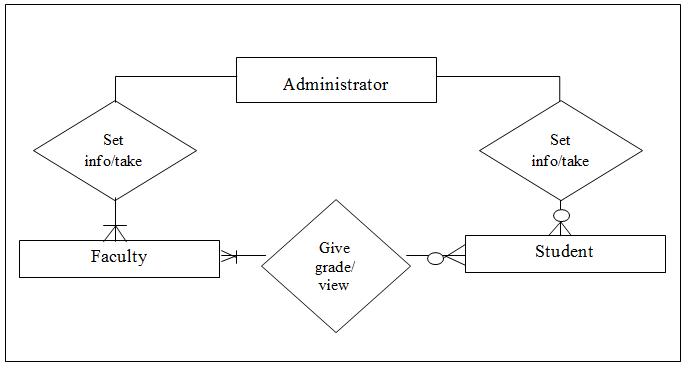
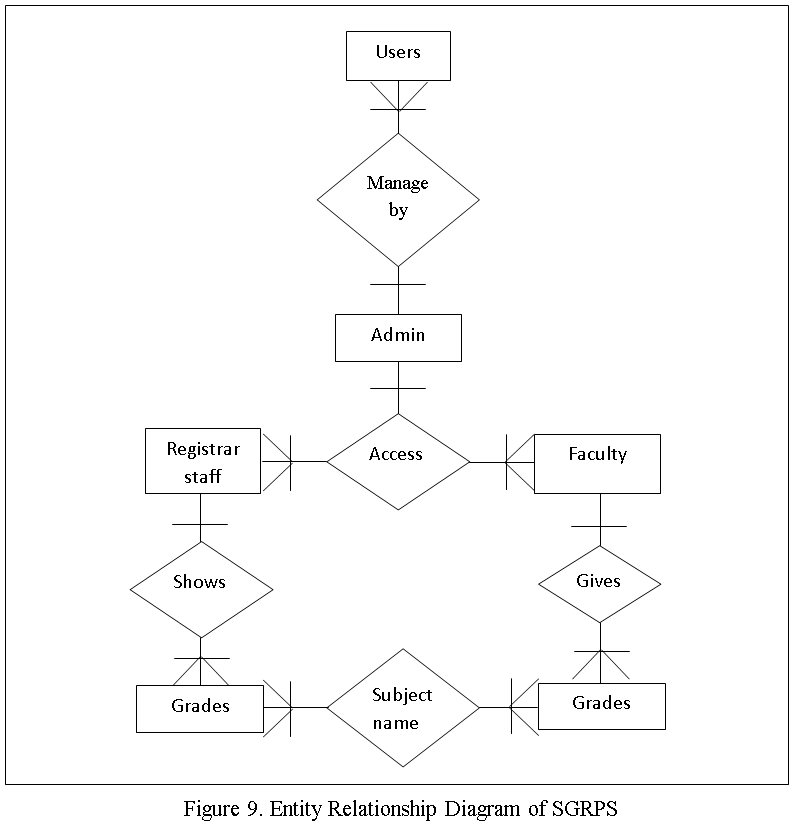
REQUIREMENTS ANALYSIS AND DOCUMENTATION
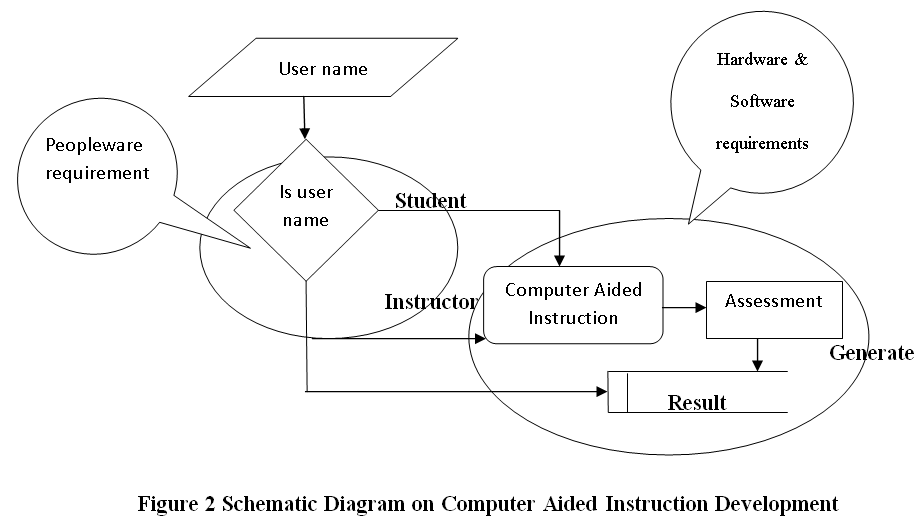
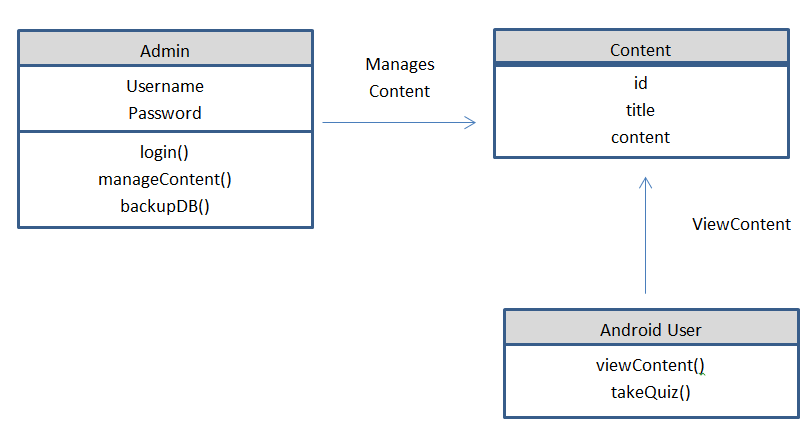
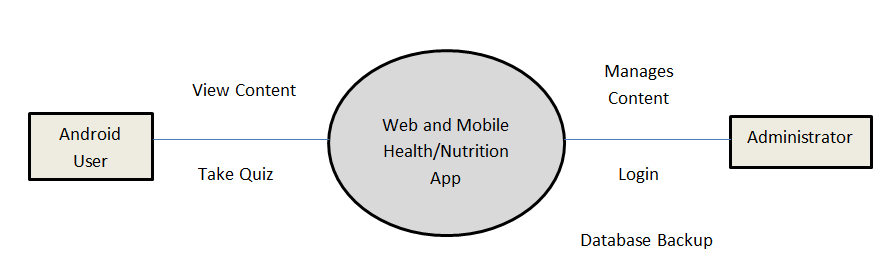
There were three requirements in this study, first was the hardware requirement, this requirement refers to the physical components of the computer system which was being used to run and execute the computer aided instruction system. Second requirement was the software requirement which was refers to the non-physical components of the computer system which was being used to develop the computer aided instruction system. Third and the last requirements was the people ware requirement which was refers to the people who have knowledge and skills in computer system operation and categorized into two types of users the administrator and student that has an ability and willingness to learn this computer aided instruction system.
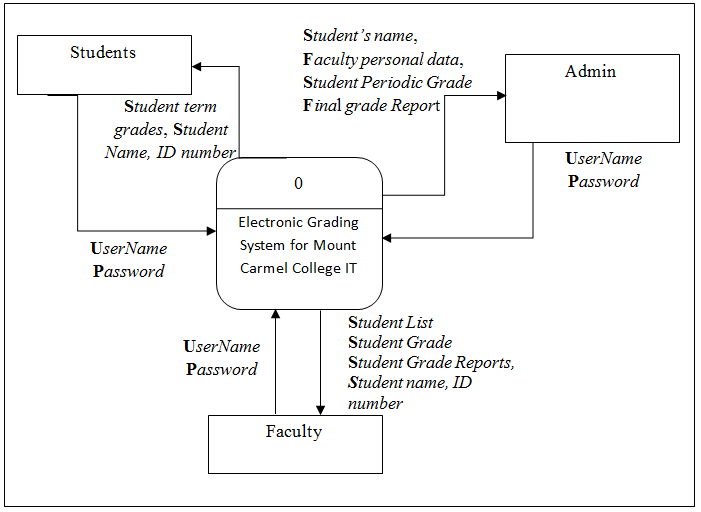
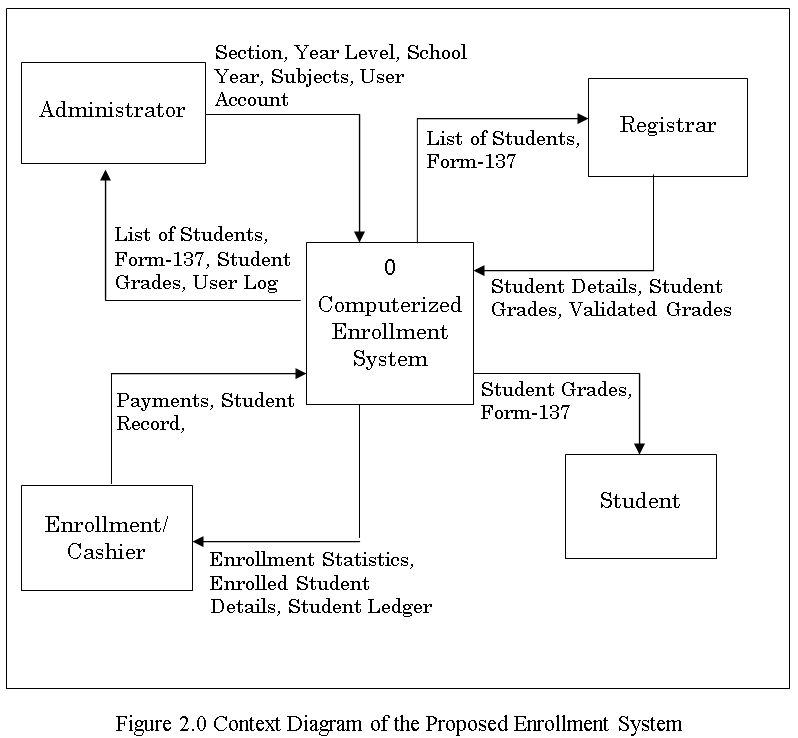
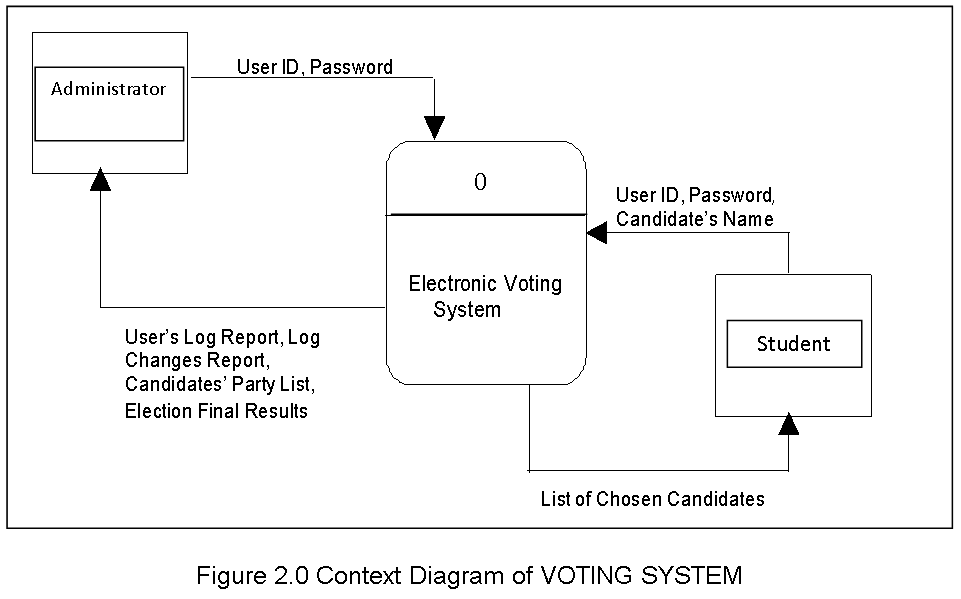
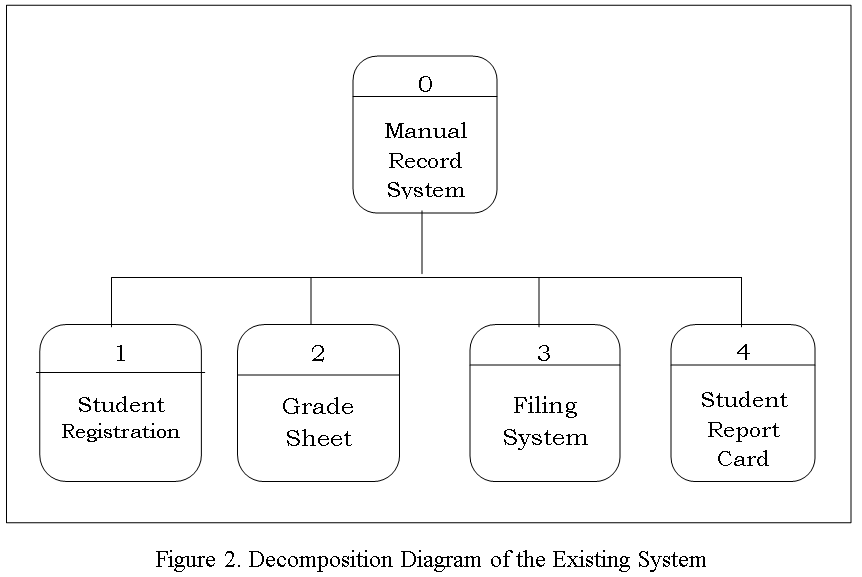
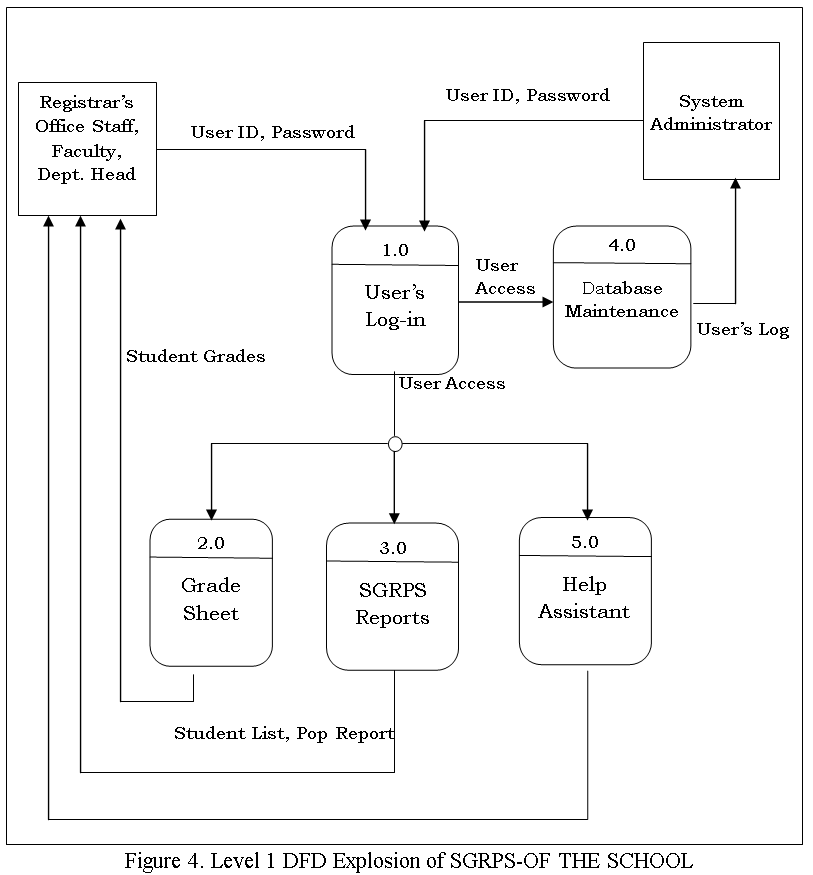
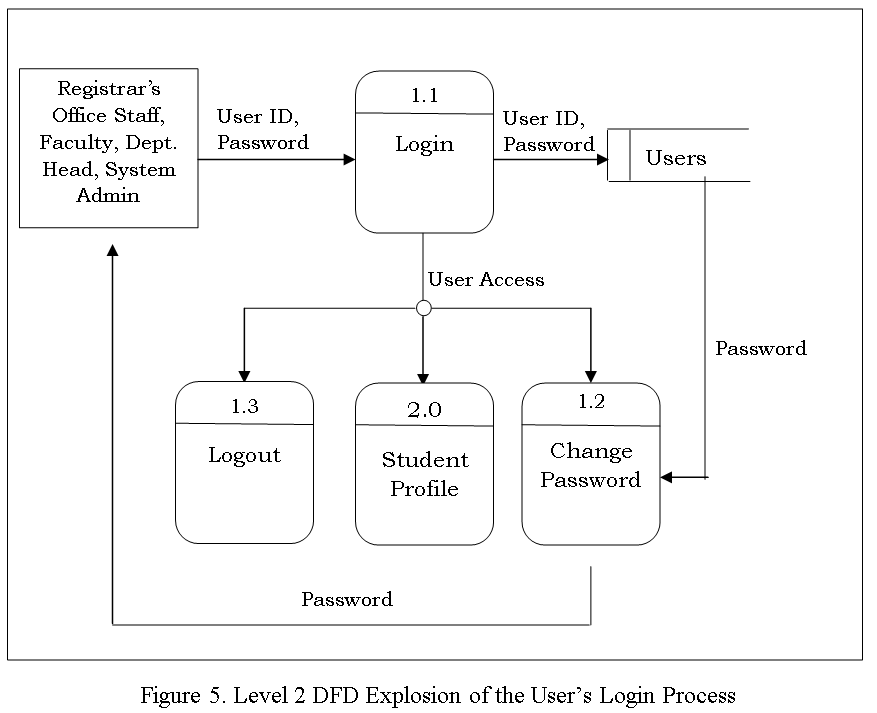
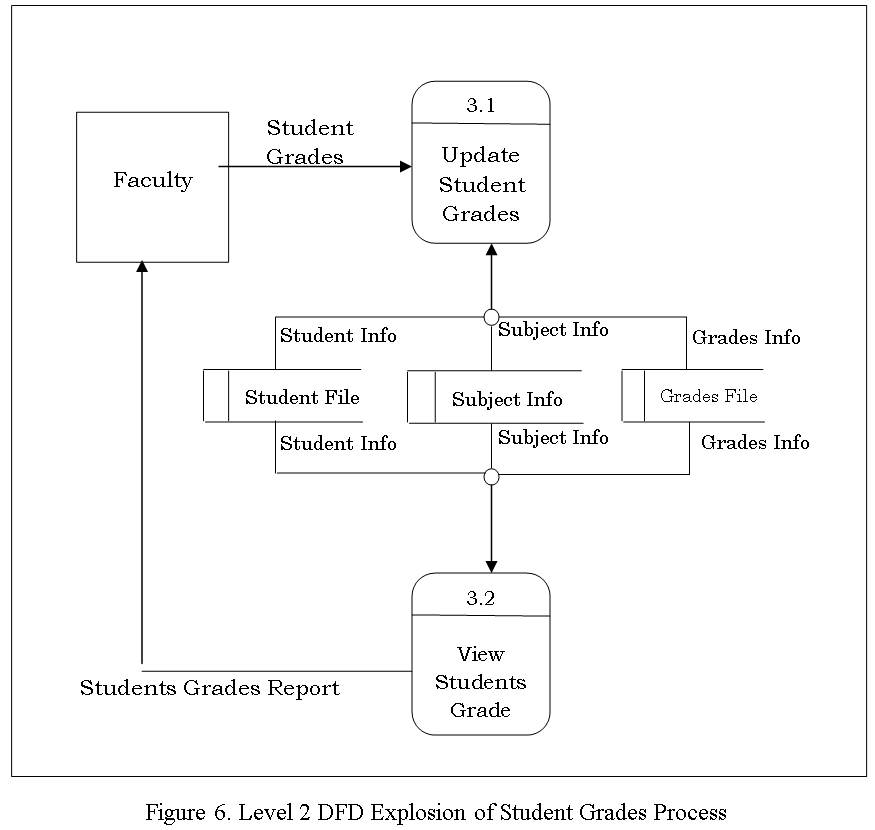
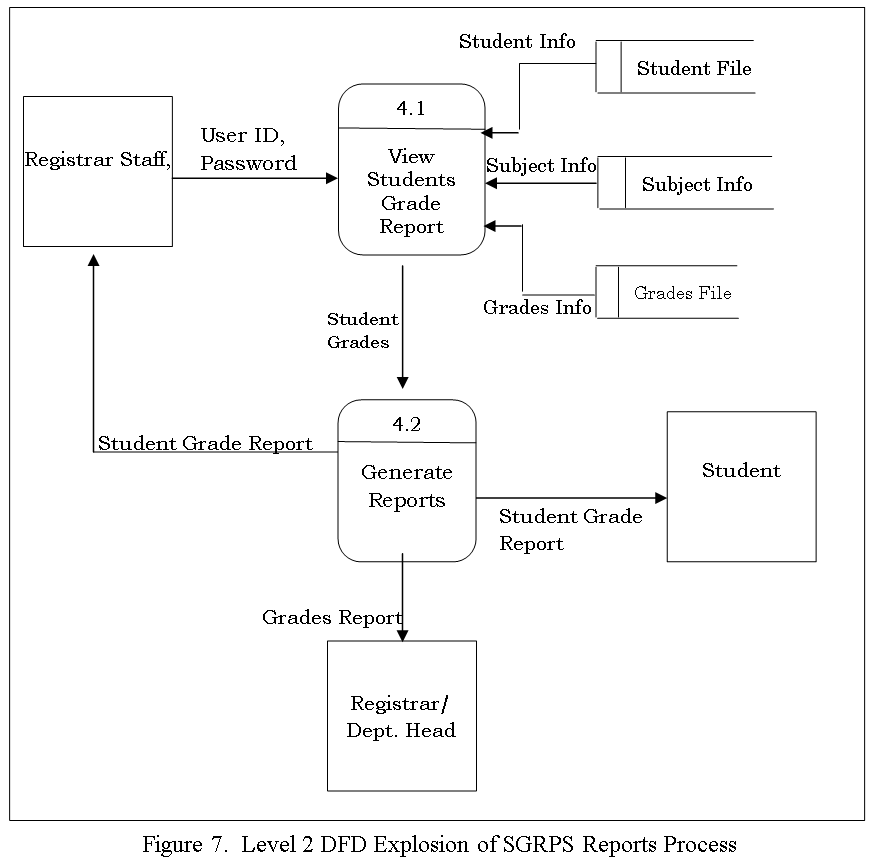
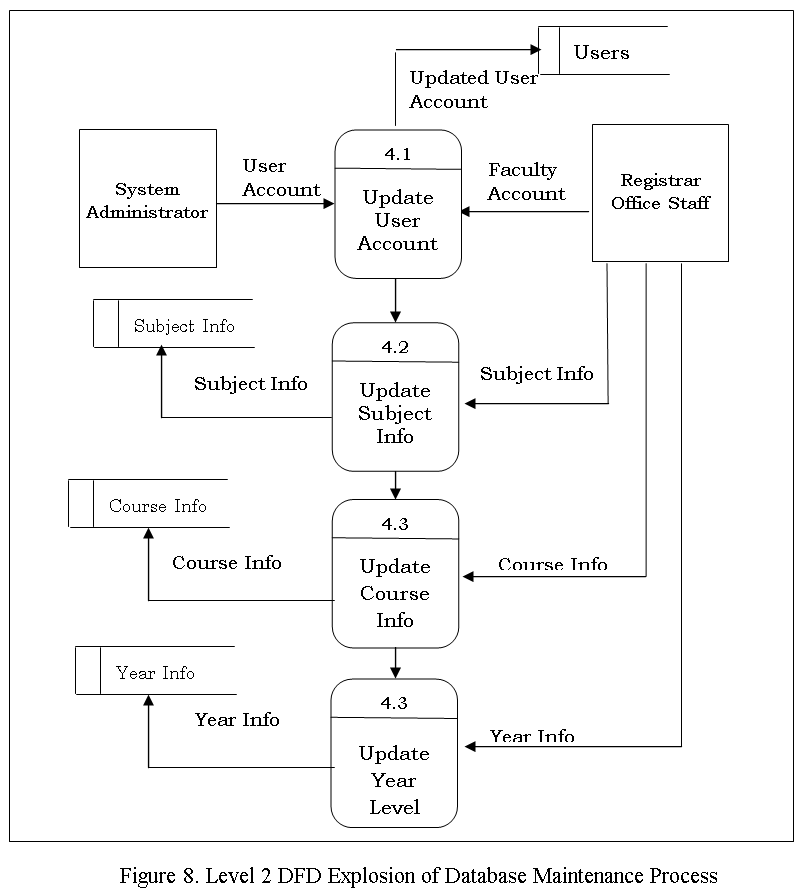
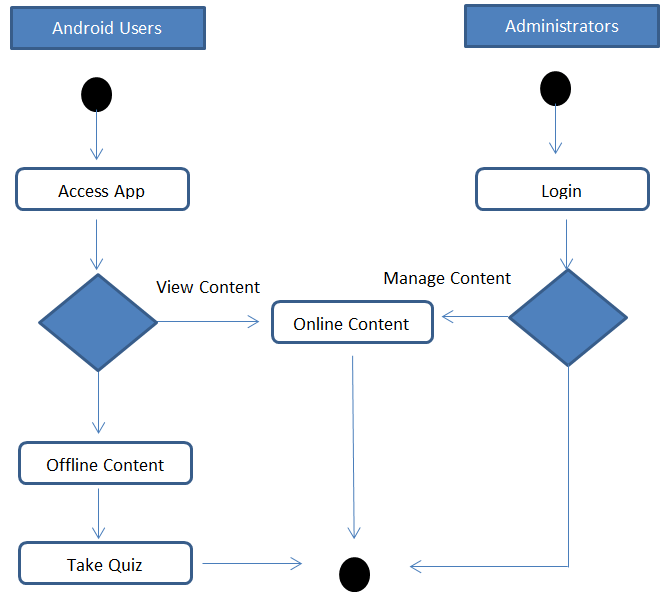
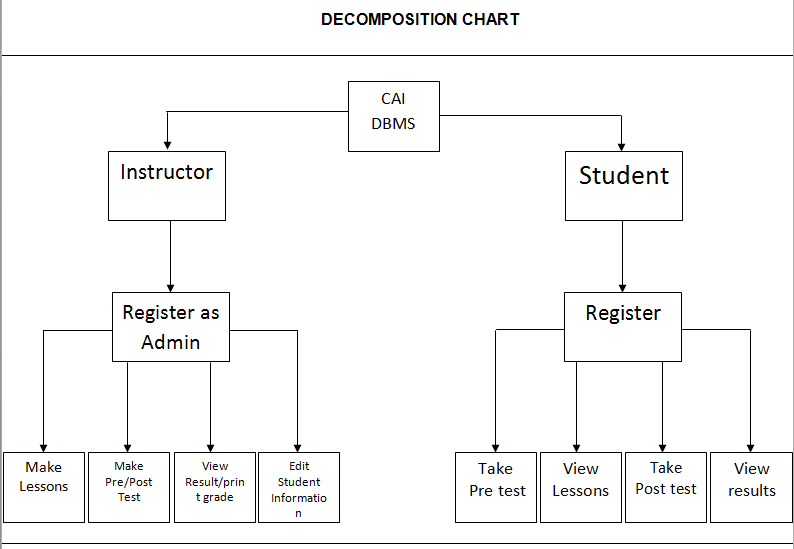
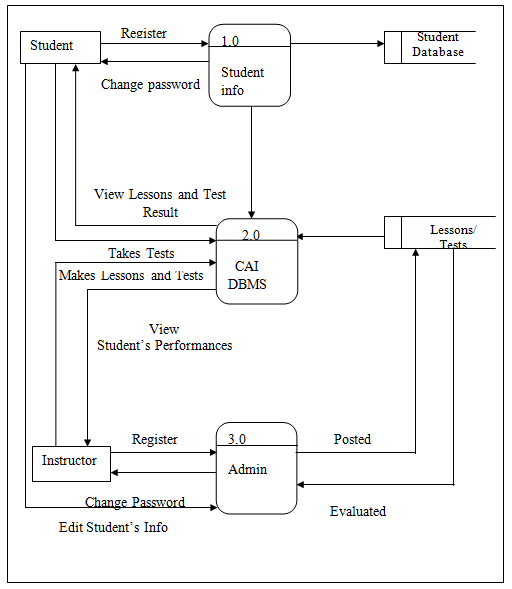
The Data Flow diagram shown below refers to the development of Computer Aided Instruction and requirements. Figure 2 shows the Decomposition of Computer Aided Instruction in Web-based Application Development subject
![Schematic Diagram on Computer Aided Instruction Development]()
Schematic Diagram on Computer Aided Instruction Development
Figure 2 Schematic Diagram on Computer Aided Instruction Development
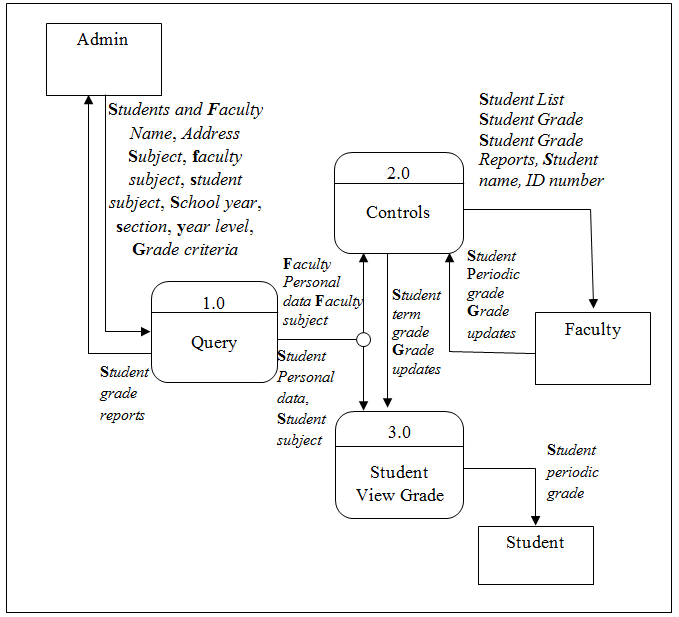
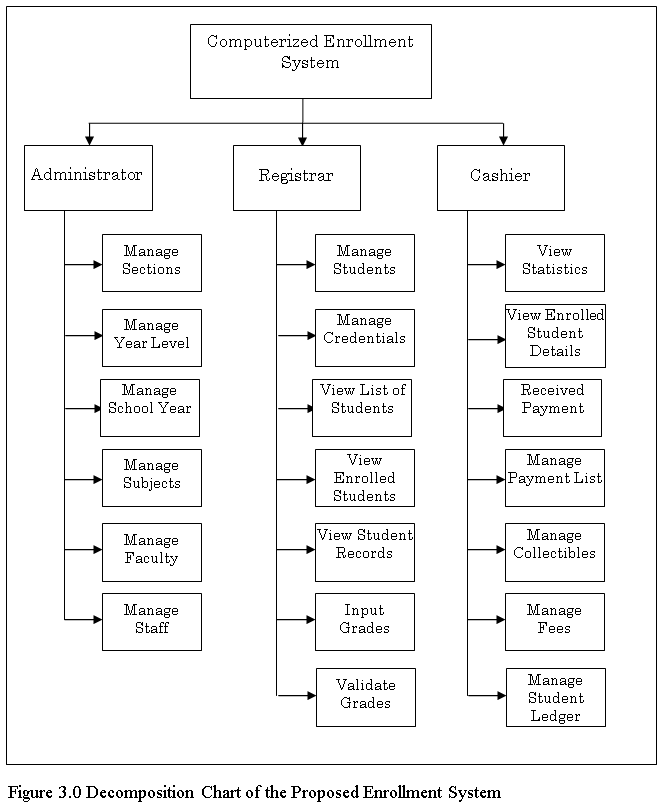
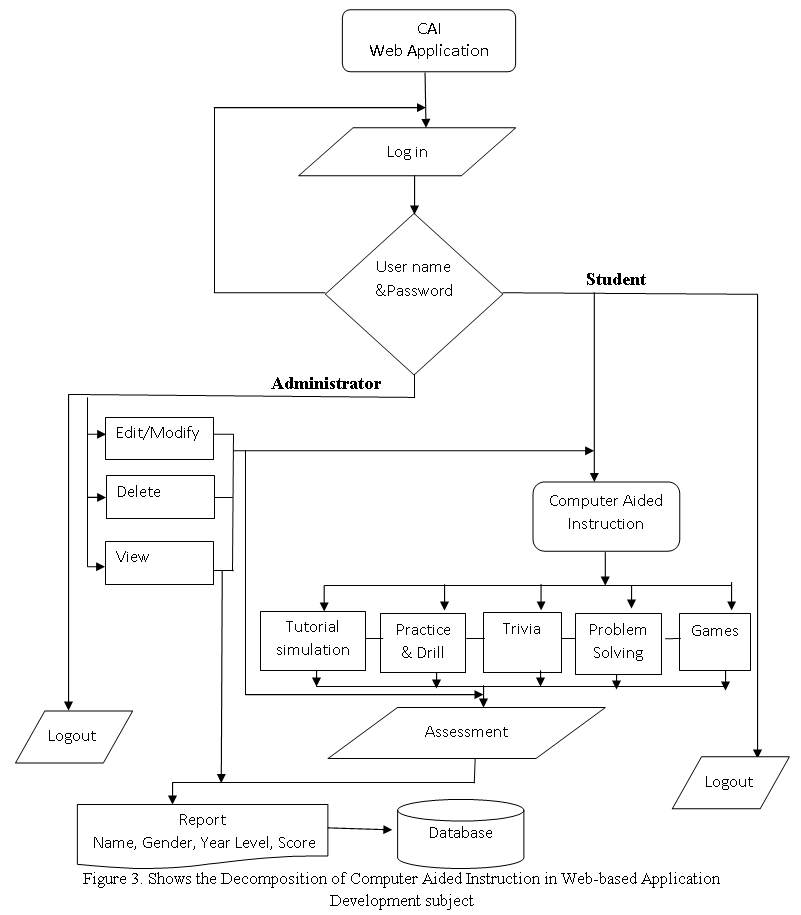
DESIGN OF SOFTWARE WITH PROCESSES
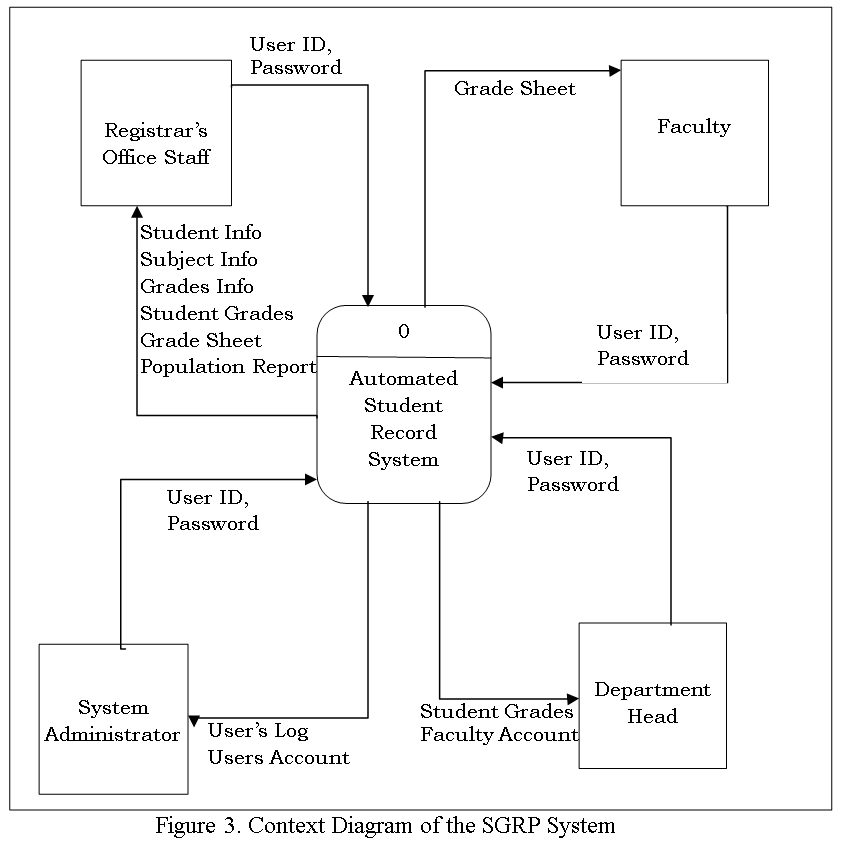
![Decomposition of Computer Aided Instruction in Web-based Application Development subject]()
Decomposition of Computer Aided Instruction in Web-based Application Development subject
The Data Flow diagram shown below refers to the development of Computer Aided Instruction and requirements. Figure 3. Shows the Decomposition of Computer Aided Instruction in Web-based Application Development subject
The CAI Web-based Application Development Subject has a login page to choose admin and user to proceed on the home page. An Admin Page which can Administer all the blocks and editing data on your CAI Application, while the User Page are the page for the user. Logout allows you to Exit the CAI Application. Edit/Modify allow admin to add, edit, update user and Admin account And lessons that put on your CAI Application. View Assessment record of the Student’s.
DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING
Hardware Requirements
Below are the recommended lists for hardware specification for the development of the end user of the proposed system.
Monitor :(LCD/LED) 15” or 17”
Processor : Intel Pentium 4 1.2 GHz or equivalent to higher specification
Motherboard : P4 built-in Audio/Video/LAN or higher
Memory : RAM 512 Mb or higher
Hard disk : 80 GB or higher
Speaker : Edifier Speaker or any type
UPS : 120 Volts. of any brand (optional)
Mouse : USB Optical Mouse or of any brand
Keyboard : Ps/2 or USB support keyboard of any brand
Optical Drive : 16X Supper Multi Drive or Equivalent
Software Requirements
Below are the recommended lists for software specification for the development of the end user of the proposed system.
Operating System : Windows 97 or higher version
Microsoft Office Package : MS Package 97 or higher
Visual Basic : 6.0 version enterprise
People ware Requirement
The targets of this system development are mainly the Information Technology students and Faculty of the school for their web-based application subject.
The researcher conducted a survey to the respondent to know if the system is needed in the Department. Researcher conducted the following testing: expert testing and user’s acceptance or final testing. Before the researcher conducting the testing, the following unit will be provided by: unit testing, integration testing and system testing to test if the researcher developed the right and exact system that they conduct.
In Unit testing, separate the part of the system. Each part is being tested individually and examined if it is working properly. By testing each part of the system. Integration Testing, the purpose of the integration testing to detect any inconsistence between the software units to integrate together. System testing is performed on the entire system where in all of the integrated software components have successfully passed in integration testing. The researcher makes an evaluation and conducted to the expert and user to navigate and to use the system to test the system functionally. Development testing, provide the syllabus and module that took from the instructor that teach web-based application development (WAD) is being used as overall references and basis in Computer Aided Instruction in Web-based Application Development Subject
User Acceptance/Final Testing
After the expert testing, the researchers prepared an evaluation which is the User Acceptance Evaluation Form (see Appendix B). This survey questionnaire is intended to the respondents of the study. To ensure validity and reliability of the survey questionnaire, it was validated by the two (2) knowledgeable IT experts with enough background in Web-based application development (1) English instructor to check the grammar of each questions. This survey questionnaire is to test reliability of the developed Web-based Computer-Assisted Instruction in Computer Hardware if the desired functions were met. Table 1.0 shows the number of respondents for the CAI-WAD.
The respondents of this study are namely; the IT Department Professors who teaches the subject Computer Organization and the Third Year IT Students in school main campus.
The total number of IT students in SCHOOL main campus is six hundred fifty nine (708) based on the population recorded in the Student Information Automated System (SIAS). Out of the total number, only Third Year IT Students with two hundred three (203) have the subject of computer hardware and were taken as respondents and three (3) IT Department Professors. The researchers just took three (3) IT professors, those professors that have the computer hardware subjects just to test the system, and later on all of the IT Professors can use it.
Plan and Implementation of Computer Aided Instruction on Web-based Application subject
The first step in implementing computer-aided instruction was to identify the skills or behaviours that you want to teach via the computer. The learner’s Individualized Family Service Plan (IFSP) or Individualized Education Program (IEP) will specify priorities and specific goals. From a review of the listed goals and discussion with learners and their families and team members, a specific skill (e.g., improved spelling, increased vocabulary) or behaviour (e.g., recognizing the emotions of other people during conversations) should be identified as the target of instruction. It is important to operationalize the behaviour or skill so that it was observable and measurable.
The steps for implementation of computer-aided instruction are actually guidelines for the general use of computer software for instructional purposes. Thus, the steps for the use of specific software will vary according to the instructions that accompany purchased software.
Identifying the Target of Instruction refers to a learner’s IEP or IFSP to identify the learner’s goals that will be the target of instruction and operationalize it so that it will be observable and measurable.
Collecting Baseline Data refers to the collection baseline data appropriate for the targeted skill.
Once the specific skill has been identified and operationalized, gather baseline data on the learner’s use of the skill. Data may be gathered by multiple methods, depending on the skill or behaviour. For targeted skills, such as recognizing and correctly interpreting the data pre-test and post-tests may be used to determine the efficiency of Computer Aided Instruction on Web-based Application subject, the effectiveness from education computer instruction and learners satisfaction.
Identifying Technology Support refers to the identification technology and support personnel in the implementation of this study.
Before proceeding with the purchase of computer software, identify and contact persons who provide computer support. These individuals may be official technology support persons or others who have different titles but were experts on all things related to computers. The information these individuals have is invaluable, and establishing a working relationship with them is a great investment.
Identifying Available Computers for Use refers to gathering information about general computer specification, computer availability, classroom, media centre and schedule for the learner’s.
Prior to investing time, money, and effort in acquiring software that addresses the target of instruction, identify and schedule computers for learners to use.
Once all information gathered about available computers, check classroom and school-wide calendars to identify times that computers may be used by the learners. Create a schedule for the learner’s use of available computers and share this information with appropriate staff.
Identifying Appropriate Software refers to the checking the availability of software on existing accessible computer, programs about how to use the system.
Computer-aided instruction on web-based application subject may be selected as an evidence-based instructional strategy because the learner already has an interest in computers or because of the availability of software to teach the targeted skill or behaviour.
Selecting and Installing Software refers to the installation of the actual software used in the proposed system explicitly for instructors and students as target skills and behaviour.
Learning the Software refers to building of program that match with the learners’ interest and abilities.
Completing a Task Analysis of Steps for Using Software refers to the analysis of the steps for accessing the designated software with in computer aided instruction and creation of a trouble-shooting guide for the software and provide t to learners.
Task analysis is an important step in CAI, because helps enable learners to use computers more independently. This task analysis is specific to how to use the computer software that is installed and should not be confused with a task analysis of the targeted skill.
Teaching the Software to Others Who Support the Learner refers introduction of the software to those who work with the learner at school.
At this point, it is appropriate to introduce the software to those who work with and support the learner. This may include other teachers, classroom assistants, and peers. Explain how the program addresses to the target skill. Provides an overview of the task analysis and of the program.
Introducing Learner to Software refers to the determination on how the proposed system helps the learners and the instructor on the target skills. Learners and instructors interact with the system and provide feedback and assistance.
Providing Learners with Multiple Opportunities to Use Computer refers to the regular schedule of the learners and instructor in using the system.
It is very important for the learners and the instructors to have on-going opportunities to practice the targeted skill or behaviour with the CAI system.
Providing On-going Support to Learners giving an opportunity to the learners of having an access to staffs or instructors for the assistance and to answer the question during CAI time. As learners become more independent with the use of the computer and the specific software program, you may find that they do not need on-going supervision or assistance. If that is the case, celebrate! Regardless of how adept learners are in accessing and engaging in CAI, it will be important that they know how to seek assistance from a staff member or peer should they need help at any point.
Collecting Data on Acquisition of Target Skill refers to the collection of data on the target skill in a format similar to baseline data collection for instructional decision regarding the target skill of behaviour
The collection of data on the acquisition of the target skill during the use of CAI is as important as the initial collection of baseline date. As mentioned in Step 2, you may find that the program has a data collection mechanism. These data may prove useful for providing learners with immediate feedback as they use the software and may also be useful to share with the learners’ families and others on their team. Again, do not rely on these data alone for monitoring learner progress toward goals. Using the same procedures that were used to collect data at baseline, continue to collect data regularly on how the learner uses and generalizes the target skill being taught or supported via CAI. That is, in addition to any information gathered by the computer program, also assess the learner’s use of the target skill or behaviour in school and other environments
IMPLEMENTATION RESULT
The result of this study will be the basis of recommending of the implementation of the Computer Aided Instruction on Web-based Application subject for instructors and students of the institution.
![]()